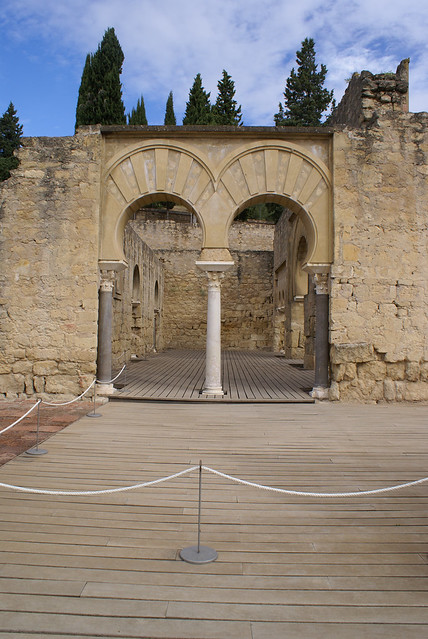
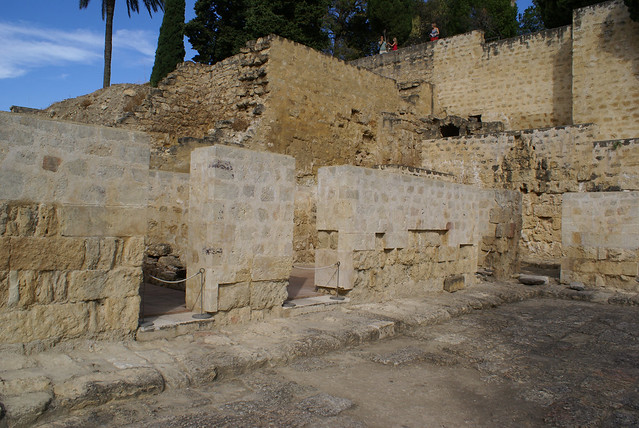
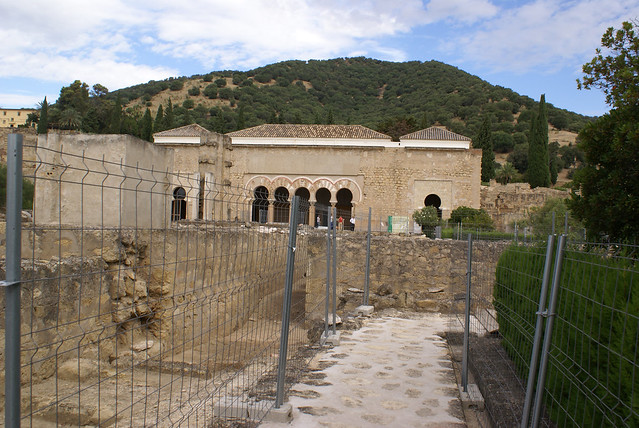
Bellatrix, a star in the constellation of Orion, is a hot, blue giant some 240-250 light years away; let’s, for the sake of argument, call it 245. This would mean that the light from the star we see today, left in 1770 and has in that time been travelling at 186,000 miles per second. To put that in perspective, light can travel 7 times around the Earth in a single second.
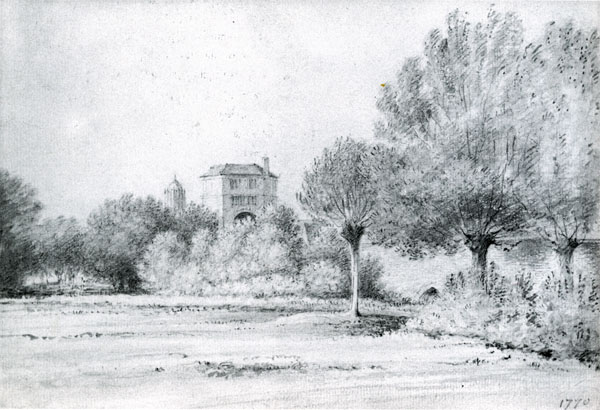 |
| A view of Friar Bacon’s study, Oxford (1770) by John Malchair |
Such a speed and distance is pretty much beyond the scope of even the keenest imagination. It’s hard to comprehend for example that at the time of the French Revolution, the light from Bellatrix had already been travelling 19 years. That during the Great Exhibition, it was 71 years into its journey. And that at the start of the First World War it had been going for 144 years, still at a speed way beyond our comprehension.
And for another 100 years it has travelled; at 186,000 miles a second.
In contemplating the distance it has travelled, thinking in terms of major events doesn’t really help; after all, we don’t conceive of history in terms of seconds, and thinking of the speed of light outside a few seconds is difficult (669,600,000 miles per hour…?)
Recollecting events in my life however – from my earliest memories on a beach on the Isle of Wight, through nursery, primary school, the Queen’s Silver Jubilee, holidays in Swanage, Christmases, birthdays, sleep overs at my Nan and Grandad’s, church events, middle school, upper school, university, relationships, friendships, nights in the pub etc. – I can better imagine the passage of time, which, ironically, makes it more difficult to comprehend the distance light travels. I can do the same with regards my parents’ lives and, to some extent, my grandparents, but it becomes quite impossible beyond that.
Flicking through data on historic events of the last 245 years, the mind really begins to bubble:
1775 – American War of Independence
1780s – Start of the Industrial Revolution
1787 – First convicts sent to Australia
1796 – Jenner’s smallpox vaccination
1805 – Battle of Trafalgar
1829 – Peel establishes Police force
1832 – Great Reform Act
1837 – Queen Victoria ascends the throne
1851 – The Great Exhibition
1854-56 – The Crimean War
1859 – Origin of Species published
1863 – London Underground opens
1876 – Invention of the telephone
1887 – Invention of the gramophone
1901 – Death of Queen Victoria
1912 – The Titanic sinks
1914-18 – World War I
1920 – Demonstration of television
1927 – BBC is created
1939-45 – The Second World War
1952 – Queen Elizabeth II ascends the throne
1953 – Discovery of DNA
…and so on. But it’s not until I start flicking through newspapers that my mind starts to buckle.
There’s a website where one can browse historic newspapers, and in the case of Jackson’s Oxford Journal, everything published between 1800 and 1900 is available. For example:
From Saturday, April 8, 1882:

Our photons had been travelling 112 years when Henry Long stole £95 on 17th March 1882. We can imagine him now, a young man, at the Crown Inn, seizing the chance to grab the cash. We can hear the seconds ticking away, our photons moving 186,000 miles with every tick. We can imagine Henry’s heart beating… Then we cut to the Quarter Sessions where Henry was tried. We can hear his heart beating again as the verdict is read out, the photons still zipping through space far above. Then again we cut to April 8th and picture a woman sitting at home, a clock ticking on the mantelpiece. Beyond the window, the world goes about its business, as invisibly above, our Bellatrix light journeys towards us. The woman, sitting in the room, reads the paper and the story of Henry Long. It takes 48 seconds to read, in which time our photons have moved 8,928,000 miles closer to Earth…
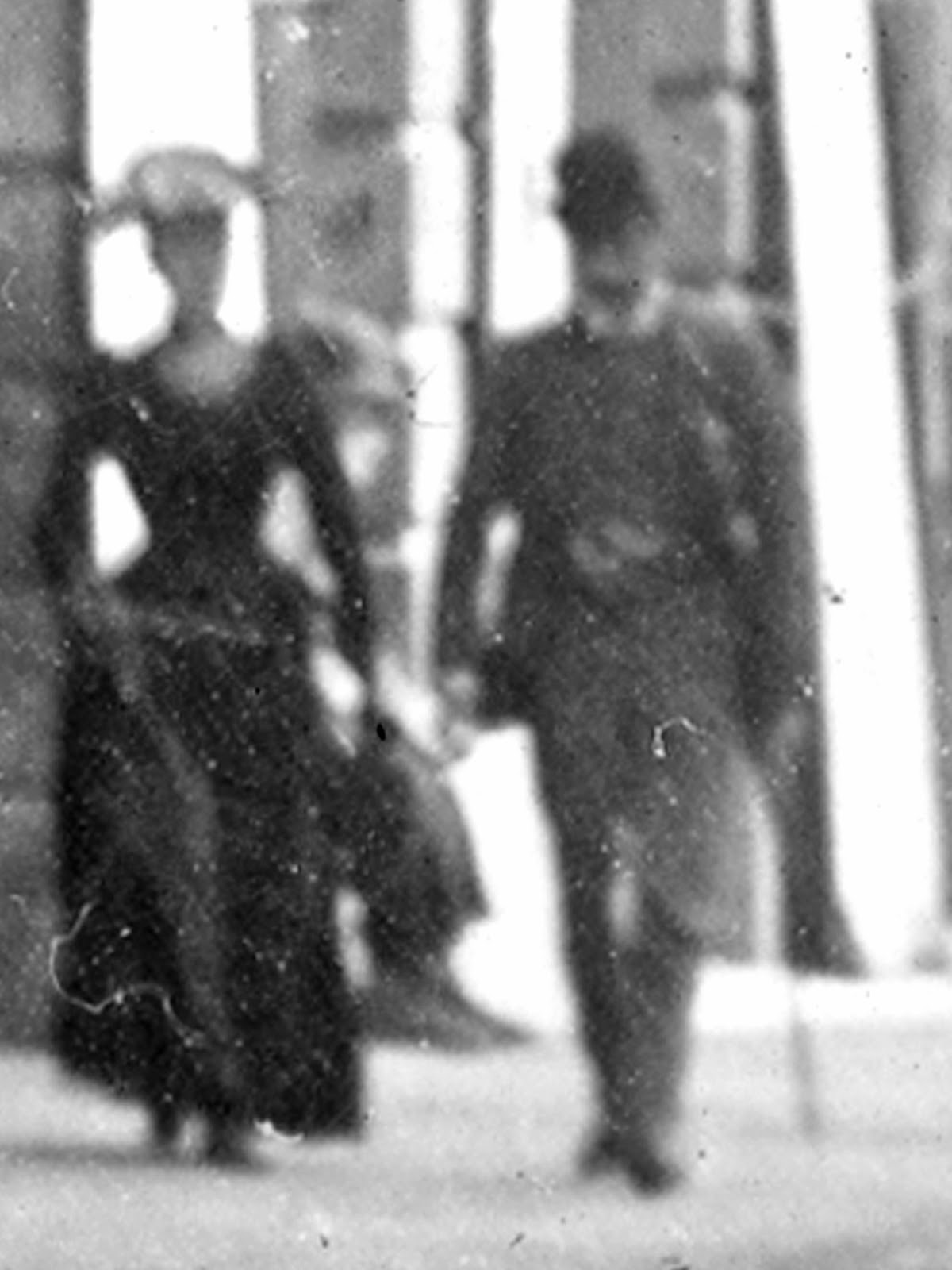
Now we leap ahead 11 years to 1893, not far from the Crown Inn, where, in the blink of an eye, the scene below is caught on camera.
Perhaps someone in the photograph below – maybe the policeman – dimly recollects the story from all those years ago,
After the photograph’s been taken, life carries on. With every step the couple take below, the light which has travelled 123 years, moves on at the same, steady pace – the equivalent of 7 times around the world…