In Tim Ingold’s Being Alive, Essays on Movement, Knowledge and Description, he writes the following:
“Recall Hägerstrand’s idea that everything there is, launched in the current of time, has a trajectory of becoming. The entwining of these ever-extending trajectories comprises the texture of the world.”
This reminded me of something I wrote some time ago about history and the relationship between history and objects:
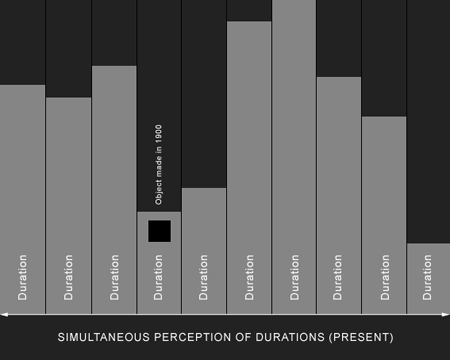
“…what we have is not a series of horizontal strata representing stacked moments in time (days, months, years, centuries etc.), but concurrent vertical lines, or what I have called ‘durations’ where each duration is an object, building or landscape feature and where the present is our simultaneous perception of those that are extant (of course, in the case of buildings, individual objects can also contain many separate durations).
It was Bill Viola who said that ‘we have been living this same moment ever since we were conceived. It is memory, and to some extent sleep, that gives the impression of a life of discrete parts, periods or sections, of certain times or highlights’. Similarly we can say that every object, building or landscape feature has existed in one continuous moment and that it is to some extent the passing generations which gives the impression of the past as being a series of ‘discrete parts, periods or sections…”
This is very similar to what Hägerstrand – via Ingold – describes above and in many ways, the second diagram (above), illustrating the idea of vertical durations, is like a loom, where the durations are the warp threads and our perception of simultaneous durations are the weft, leading to an entwining of what Hägerstrand calls ever-extended trajectories making up the texture of the world.
In this analogy we are both the weft and the warp; both a duration and the perceiver of durations. We find something similar to this, again in Ingold’s writing:
“…since the living body is primordially and irrevocably stitched into the fabric of the world, our perception of the world is no more, and no less, than the world’s perception of itself – in and through us. This is just another way of saying that the inhabited world is sentient.”