Having read Tim Ingold’s book ‘Lines – a Brief History‘, I downloaded another of his books entitled ‘Being Alive, Essays in Movement, Knowledge and Description‘ as the title seemed to suggest it would be of interest to me insofar as my work on empathy and the past has found itself returning time and again to ideas of movement and knowledge; empathy is, I believe, an augmented discourse between bodily experience and knowledge, and my aim as an artist is to articulate empathy through the description of this conversation between individuals and the landscape.
“It is by moving that we know, and it is by moving, too, that we describe,” writes Ingold early on in the book, which seems to bode well for my research and my search for the form that on an artistic level my research should take .
I’ve recently been working with the form of the folded map, inspired as I’ve written before by an old trench map which I recently purchased. In particular, I’m interested in the folds of the map, the creases which show that the map was used and in the possession of an individual. In ‘Lines – a Brief History‘ Ingold draws a parallel between creases in materials such as paper and the creases one finds on the palm of your hand which reinforces the connection between owner and object.
I’ve been wondering how I can develop this idea. I’ve already completed a ‘text map’ based on observations made over the course of several walks (below) but I want to develop the idea graphically as well.
I thought about the concept of a map and what the aesthetic of the folded paper alludes to. I came up with the following:
- the idea of a specific place or of place in general
- the sense of that place – through the map object – as belonging to an individual
- the idea of the individual
- the idea of movement in and through a place whether in the past, present or future
- the idea of movement preserved in the folds
What I want to do is articulate the idea of empathy as a discourse between bodily experience and knowledge. The text map above is a document of bodily experience which when written down and presented as a ‘map’ becomes knowledge which other individuals could theoretically use. Its shape and its folds allude both to the idea of place and of possession (the concept of an individual as a place is something else which I’ve been exploring over the past few years). But what about the circular nature of experience and knowledge?
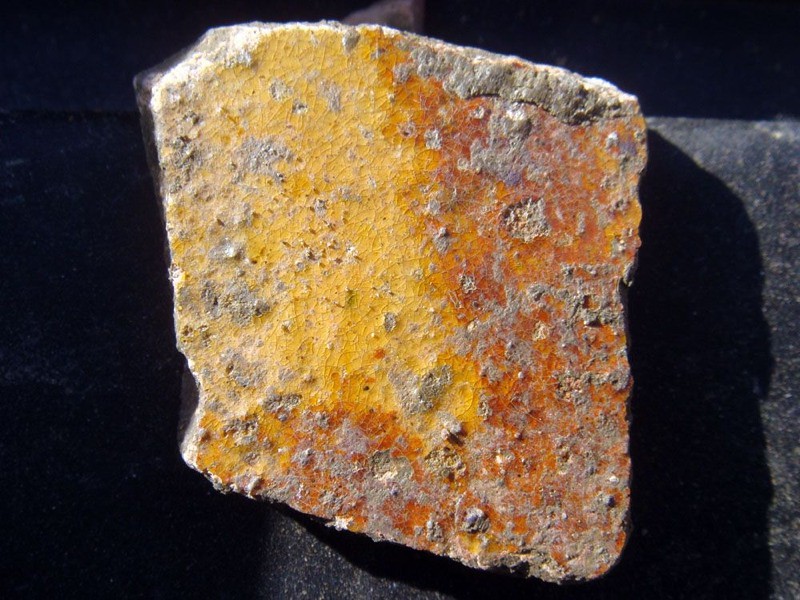
The fact is, when we think about the past, we can only ever build a picture through tiny fragments – whether pieces of pot, miscellaneous artefacts like coins, pieces of text, letters and anecdotes (unfolding through enfolding). Each of the phrases on my text map is a fragment from which the wider picture can be extrapolated, just as with a fragment of pot, one not only builds an image of the pot but extrapolates the wide world to which it once belonged.
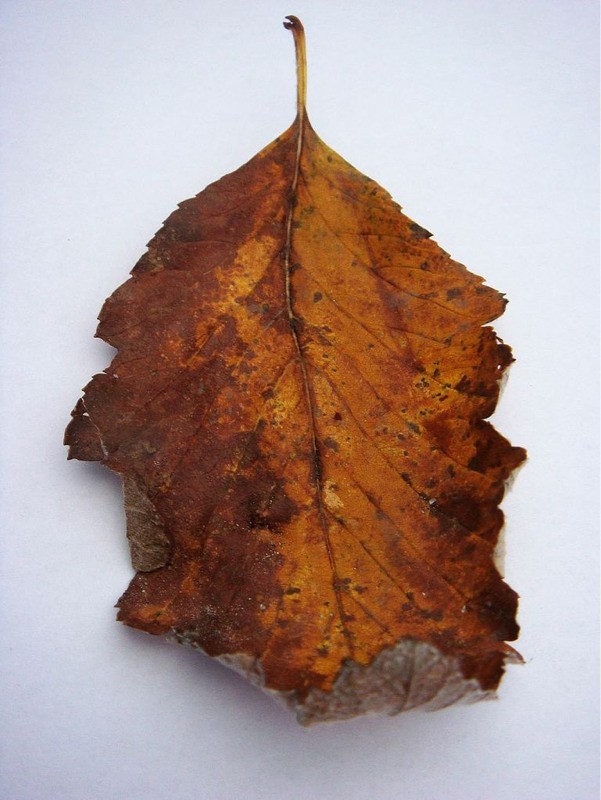
The piece of pottery has something in common with the phrase: “leaves drowned in disappearing puddles”which I noted on one of my walks. It is also interesting that when I found the above piece of pottery, I also discovered – almost at the same time – a leaf, which was almost identical in colour. The transient nowness of the leaf then, serves – through its colour – to articulate the idea of the fragment of pot as being similar to the fragment of text.